Conservation Genetics Laboratory
Our conservation genetics research addresses threats to cetaceans, fish, and coastal carnivores.
The Conservation Genetics Lab is an integral part of Raincoast’s efforts to protect the land, waters and wildlife of coastal BC. The DNA and RNA analysis we perform provides our scientists with reliable insights into the population structure, health, diets, and resilience and genetic isolation of coastal species. The lab works closely with our Cetacean Conservation Research Program and also helps answer important questions for our other conservation initiatives.
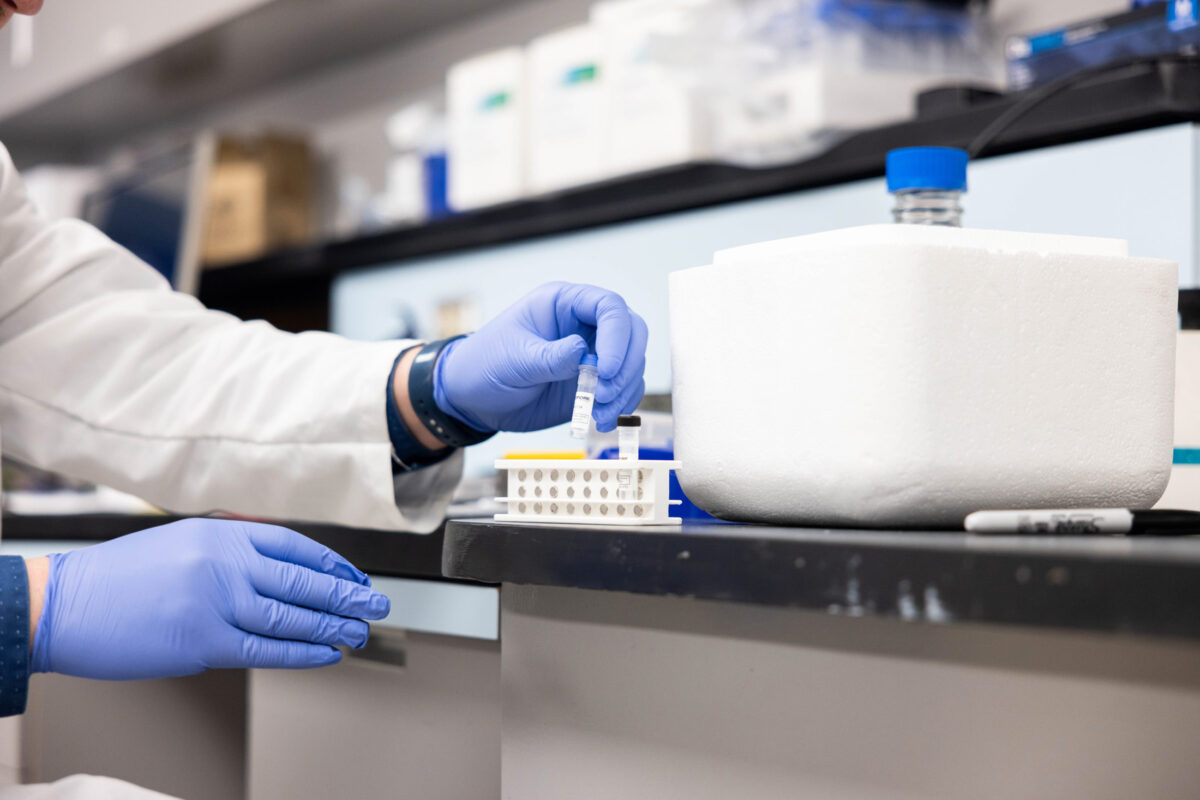


Cutting edge genetics and genomics analysis
The Raincoast Conservation Genetics Lab is equipped with a complete set of instrumentation to conduct molecular biology and genetics, including cutting-edge DNA sequencing technology. Our Research Scientist, Dr. Adam Warner, has extensive experience in genetics, genomics and DNA sequencing, has set up our lab space and has begun to carry out this research under the guidance of our Cetacean Research Program directors Dr. Lance Barrett-Lennard and Dr. Valeria Vergara. The lab works alongside Fisheries and Oceans Canada, which is hosting our lab space at the Pacific Science Enterprise Centre.
Understanding killer whale diet
A lack of sufficient Chinook salmon in the diets of Southern and Northern Resident killer whales has been linked to declines in population health. Our lab has the ability to extract and analyze salmon DNA from Resident killer whales feces, to identify the salmon stocks of most importance to the whales. Since we can identify the individual whales that produced fecal material genetically, we can link other health metrics such as stress hormone levels (also found in the fecal material) to individual killer whales.
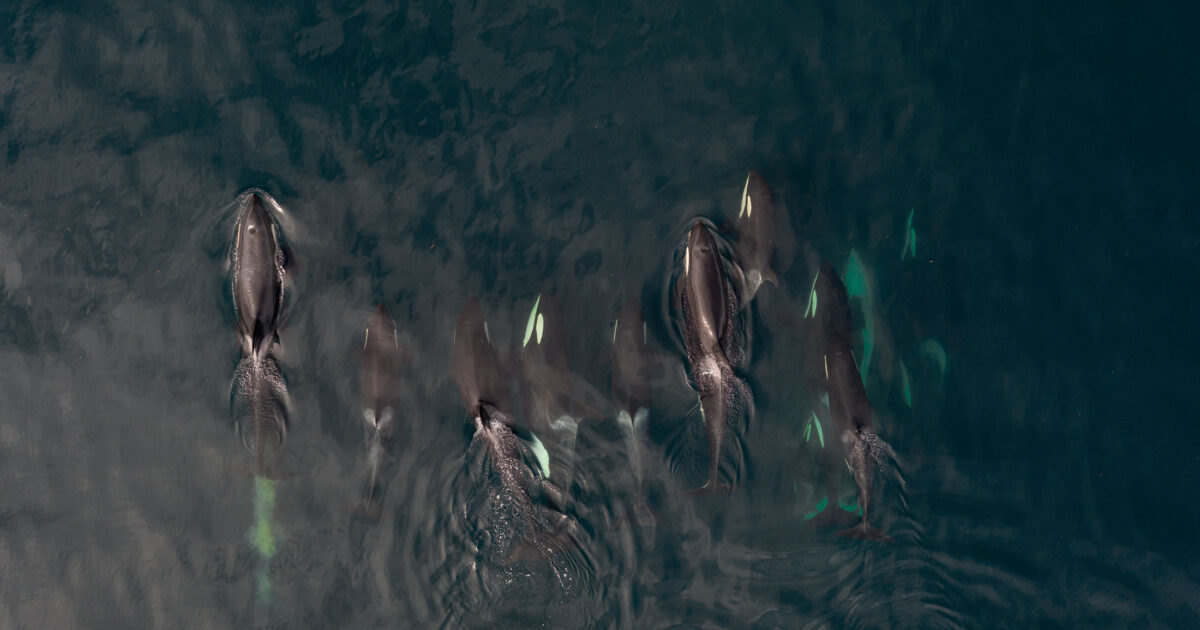

Killer whale population health and dynamics
Killer whales live in small populations that from their size alone would appear to be vulnerable to negative effects of inbreeding. We recently sequenced the entire genomes of 142 members of the Northern Resident population to directly assess inbreeding, genetic diversity, and immune system strength. We are comparing this information in this dataset to one for Southern Residents compiled by NOAA in the United States. This will help us gain insight into the comparative health of these important fish-eating populations of killer whales. We are also finalizing a study of inbreeding in marine mammal-eating Bigg’s killer whales, which will inform our understanding of similarities and differences between North Pacific killer whale populations.
Environmental DNA to aid research focused on wild salmon and coastal wolves
Our research on wild salmon and coastal wolf populations has the potential to be expanded through the use of environmental DNA (eDNA) monitoring and analysis. Through eDNA, we can track and assess salmon populations and determine abundance and diversity. Using wolf scat samples we can identify specific individuals, their sex, and the prey consumed. By learning more about these important populations, we hope to drive policy change to protect biodiversity.





